What Is a Diamond Grading Report?
A diamond grading report (also known as a diamond grading certificate) is essentially a birth certificate for a diamond, providing an independent, scientific assessment of its quality and characteristics. Issued by third-party gemological laboratories such as GCal, GIA and IGI, it outlines the 4Cs—cut, color clarity and carat weight—and may also include details like proportions, fluorescence, polish and symmetry.
Diamond grading reports are detailed by design. Familiarity with their structure and terminology ensures you know exactly what you’re selecting. This guide will walk you through the key components, so you can confidently interpret a grading report and choose the perfect diamond.
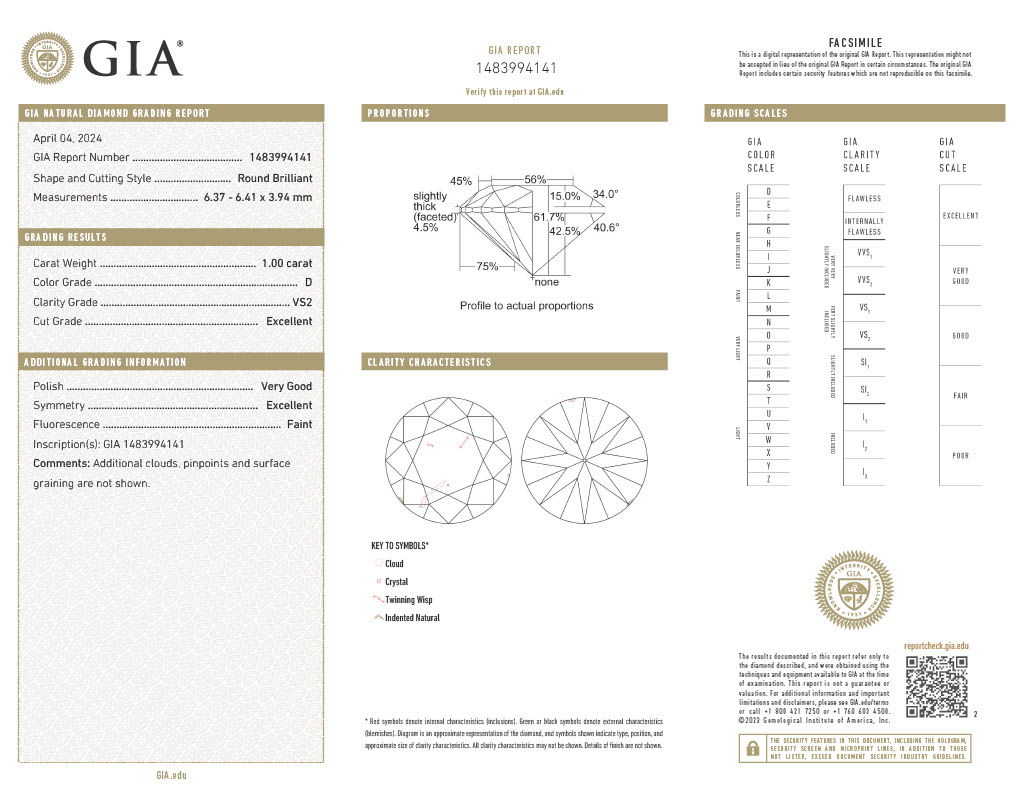
Here’s how to interpret each of the 4Cs on the certificate:
Carat weight is straightforward: it measures a diamond’s physical weight, with one carat equal to 0.2 grams. Larger diamonds are rarer, so weight often correlates with price, but size alone doesn’t determine value. On a diamond report, look for the exact weight (e.g., 1.02 ct), listed precisely to the hundredth of a carat.
On a report, cut refers not to a diamond’s shape (like round or oval) but to how well it has been crafted to reflect light. GIA assigns cut grades ranging from Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair to Poor.
Color indicates how free a white diamond is from visible tint. The scale runs from D (colorless) to Z (noticeable yellow or brown tint). Diamonds graded D-F are considered colorless and are the most desirable. G-J diamonds are near colorless and still appear bright and white in most settings. Beyond J, warmth in a diamond becomes more apparent to the eye.
Fancy color diamonds have their own unique grading system focused on richness and saturation. Learn more about fancy diamonds in this article.
Clarity evaluates the presence of internal inclusions or surface blemishes. Most are microscopic and don’t diminish the stone’s appearance. Read more about diamond clarity and what it means for your purchase in this article.
In addition to the 4Cs, a diamond grading certificate includes several other key details that speak to the stone’s artistry, appearance and authenticity.
Diamond Measurements and Proportions
The certificate will list the diamond’s physical dimensions—length, width and depth—along with proportion metrics such as table percentage, depth percentage, crown angle and pavilion angle.
Diamond Polish and Symmetry
Polish and symmetry are also provided on the diamond report. They reflect the precision and quality of the diamond’s cut and are graded from Excellent to Poor, indicating how well light reflects and refracts inside the diamond. Learn why symmetry is important in a diamond in this article.
Diamond Fluorescence
Some diamonds exhibit a soft glow when exposed to UV light. This characteristic is known as fluorescence and is described on the report as None, Faint, Medium, Strong or Very Strong. While usually subtle, strong fluorescence may affect a diamond’s appearance or market value in certain cases.
Diamond Laser Inscription
Many diamonds are microscopically inscribed with the certificate number on the girdle, providing a discreet but secure method of identification and authenticity verification.
Diamond Plotting Diagram
Often described as the diamond’s fingerprint, a plotting diagram illustrates the type and location of any inclusions or blemishes. It can be useful for verifying the diamond under magnification and serves as a reference point for future identification.
You can view a diamond’s GIA or IGI report when customizing your ring on our online ring builder. Your ring purchase from us comes standard with the diamond’s original grading report, so you can trust in its integrity.
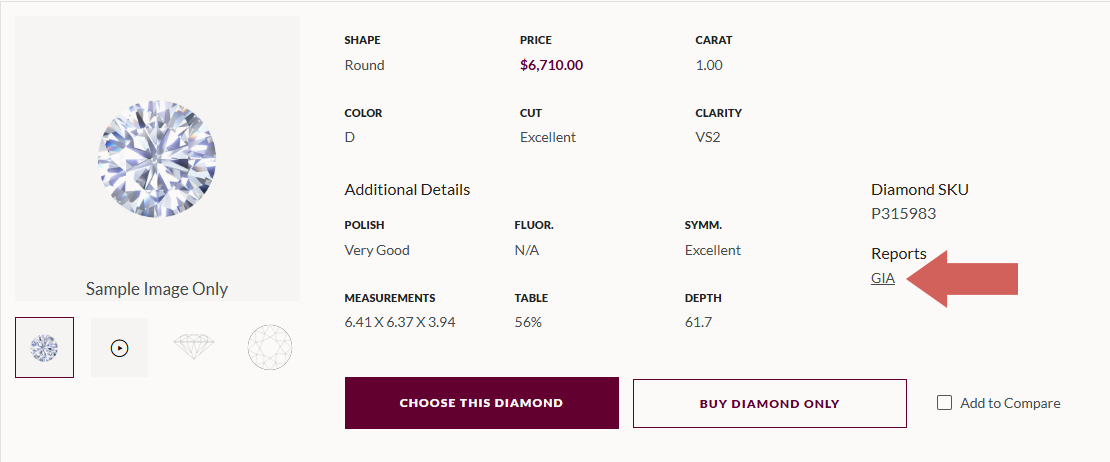
A diamond’s grading report lets you see beyond sparkle to the details that shape its brilliance and value. Explore our selection of GIA-certified natural diamonds in our online ring builder today.